What Methods Can Be Used to Dispose of Underapplied or Overapplied
Job Guild Costing
23 Determine and Dispose of Underapplied or Overapplied Overhead
Every bit you've learned, the actual overhead incurred during the year is rarely equal to the amount that was applied to the individual jobs. Thus, at year-finish, the manufacturing overhead account often has a balance, indicating overhead was either overapplied or underapplied.
If, at the end of the term, at that place is a debit rest in manufacturing overhead, the overhead is considered underapplied overhead. A debit balance in manufacturing overhead shows either that not plenty overhead was applied to the individual jobs or overhead was underapplied. If, at the terminate of the term, at that place is a credit balance in manufacturing overhead, more overhead was applied to jobs than was actually incurred. This shows the bodily amount was overapplied overhead.
The actual overhead costs are recorded through a debit to manufacturing overhead. The aforementioned business relationship is credited when overhead is practical to the private jobs in production, as shown:
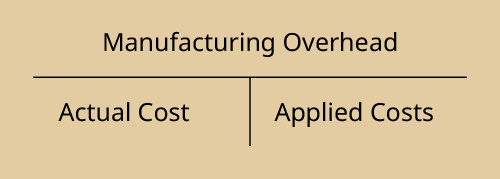
Since the overhead is first recorded in the manufacturing overhead account, then applied to the individual jobs, traced through finished goods inventory, and somewhen transferred to cost of goods sold, the twelvemonth-terminate balance is eliminated through an adjusting entry, offsetting the cost of goods sold. If manufacturing overhead has a debit balance, the overhead is underapplied, and the resulting amount in cost of appurtenances sold is understated. The adjusting entry is:

If manufacturing overhead has a credit balance, the overhead is overapplied, and the resulting corporeality in price of appurtenances sold is overstated. The adjusting entry is:

Returning to our instance, at the end of the year, Dinosaur Vinyl had actual overhead expenses of $256,500 and applied overhead expenses of $250,000, as shown:
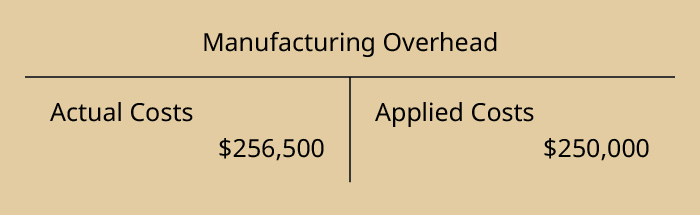
Since manufacturing overhead has a debit balance, it is underapplied, as it has not been completely allocated. The adjusting journal entry is:

If the overhead was overapplied, and the actual overhead was $248,000 and the applied overhead was $250,000, the entry would be:

To adjust for overapplied or underapplied manufacturing overhead, some companies accept a more than complicated, iii-part allocation to work in process, finished goods, and cost of appurtenances sold. This method is typically used in the effect of larger variances in their balances or in bigger companies. (You will learn more than about this in future cost or advanced managerial accounting courses.)
Kraken Boardsports
(credit: modification of images provided courtesy of Kraken Boardsports, CC BY 4.0)

Kraken Boardsports manufactures winches for snow and ski boarders to snowfall ski without a mountain or water ski without a lake ((Figure)). End-of-yr information bear witness these overhead expenses:

Kraken Boardsports had half dozen,240 straight labor hours for the twelvemonth and assigns overhead to the various jobs at the rate of $33.l per directly labor 60 minutes.
How much overhead was overapplied or underapplied during the year? What would exist the periodical entry to adjust manufacturing overhead?
Solution
The full overhead incurred is the full of:

The total overhead applied is $209,040, which is calculated as:
$33.50/direct labor hours × 6,240 direct labor hours.
The balance in manufacturing overhead is a debit residue of $210:
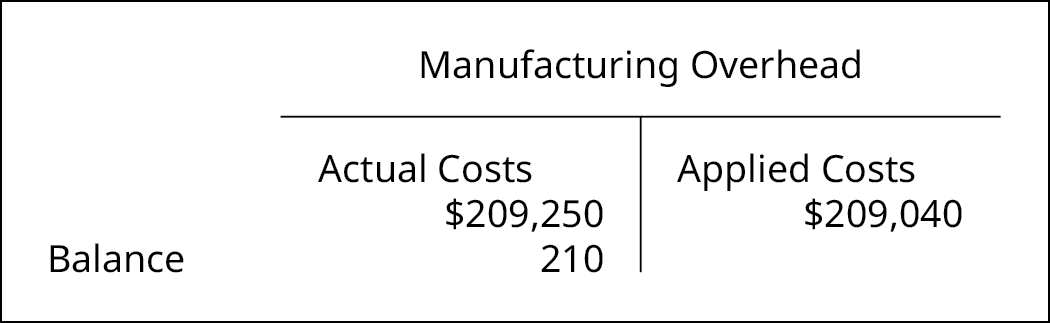
The adjusting journal entry is:

Primal Concepts and Summary
- Overhead is allocated to individual jobs based on the estimated overhead costs for the year and may be overapplied or underapplied for the year.
- Overhead is underapplied when not all of the costs accumulated in the manufacturing overhead account are applied during the year.
- Overhead is overapplied when more than overhead is applied to the jobs than was actually incurred.
- The amount of overhead overapplied or underapplied is adjusted into the cost of goods sold business relationship.
(Figure)Why is the manufacturing overhead account debited equally expenses are recognized and then credited when overhead is applied?
Expenses normally have a debit balance, and the manufacturing overhead account is debited when expenses are incurred to recognize the incurrence. When the expenses are allocated to the nugget, the piece of work in process inventory, the expense account manufacturing overhead is credited. This is in accord with the expense recognition principle. The timing of the expense follows the acquirement, and when the costs are allocated to inventory, they become a function of the product's cost and are recognized when the asset is sold.
(Effigy)A company has the following information relating to its product costs:
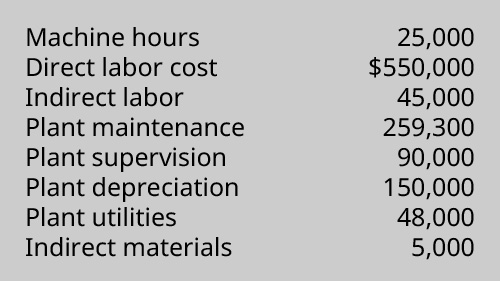
Compute the actual and applied overhead using the visitor's predetermined overhead rate of $23.92 per machine 60 minutes. Was the overhead overapplied or underapplied, and by how much?
(Figure)Coop's Stoops estimated its annual overhead to be $85,000 and based its predetermined overhead rate on 24,286 direct labor hours. At the end of the year, bodily overhead was $90,000 and the total direct labor hours were 24,100. What is the entry to dispose of the overapplied or underapplied overhead?
(Figure)Mountain Peaks applies overhead on the basis of motorcar hours and reports the following data:
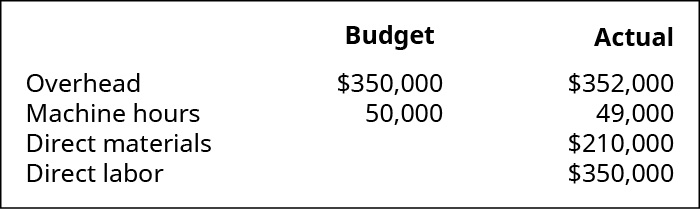
- What is the predetermined overhead charge per unit?
- How much overhead was practical during the twelvemonth?
- Was overhead over- or underapplied, and by what amount?
- What is the journal entry to dispose of the over- or underapplied overhead?
(Figure)The bodily overhead for a company is $74,539. Overhead was based on 6,000 direct labor hours and was $two,539 underapplied for the year.
- What is the overhead application charge per unit per straight labor hr?
- What is the journal entry to dispose of the underapplied overhead?
(Effigy)When setting its predetermined overhead awarding charge per unit, Tasty Box Meals estimated its overhead would be $100,000 and would crave 25,000 automobile hours in the next yr. At the end of the year, information technology found that actual overhead was $102,000 and required 26,000 machine hours.
- Determine the predetermined overhead rate.
- What is the overhead applied during the yr?
- Prepare the journal entry to eliminate the underapplied or overapplied overhead.
(Figure)Queen Bee'south Love, Inc., estimated its almanac overhead to exist $110,000 and based its predetermined overhead rate on 27,500 straight labor hours. At the finish of the year, bodily overhead was $106,000 and the total direct labor hours were 29,000. What is the entry to dispose of the overapplied or underapplied overhead?
(Effigy)Mountain Tops applies overhead on the ground of direct labor hours and reports the following information:
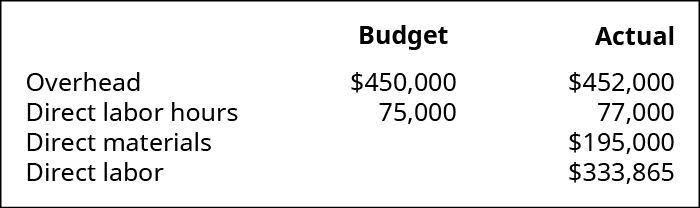
- What is the predetermined overhead rate?
- How much overhead was applied during the year?
- Was overhead overapplied or underapplied, and by what corporeality?
- What is the journal entry to dispose of the overapplied or underapplied overhead?
(Figure)The actual overhead for a company is $73,175. Overhead was based on four,500 machine hours and was $3,325 overapplied for the year.
- What is the overhead application rate per straight labor hr?
- What is the journal entry to dispose of the underapplied overhead?
(Figure)When setting its predetermined overhead application rate, Tasty Turtle estimated its overhead would be $75,000 and manufacturing would crave 25,000 machine hours in the adjacent yr. At the terminate of the year, it found that actual overhead was $74,000 and manufacturing required 24,000 car hours.
- Make up one's mind the predetermined overhead charge per unit.
- What is the overhead applied during the year?
- Prepare the journal entry to eliminate the under- or overapplied overhead.
(Figure)If a company bases its predetermined overhead rate on 100,000 automobile hours, and it really has 100,000 machine hours, would there exist an underapplied or overapplied overhead?
Glossary
- overapplied overhead
- situation when the overhead practical to the individual jobs is greater than the actual overhead; when overhead is overapplied, the manufacturing overhead has a credit balance
- underapplied overhead
- situation when the overhead applied to the private jobs is less than the actual overhead; when overhead is underapplied, the manufacturing overhead has a debit balance
Source: https://opentextbc.ca/principlesofaccountingv2openstax/chapter/determine-and-dispose-of-underapplied-or-overapplied-overhead/
0 Response to "What Methods Can Be Used to Dispose of Underapplied or Overapplied"
Post a Comment